 02 Feb,2026
02 Feb,2026
Is Your Dust Collector System Truly Efficient and Compl...

1. Main forms of adsorption and desorption
Adsorption is the process of adsorbents accumulating or condensing one or more components in a gas mixture on the surface to achieve separation. Commonly used adsorbents include granular activated carbon, honeycomb activated carbon, activated carbon fiber felt, honeycomb zeolite, zeolite wheel, etc. The purification efficiency of the adsorption method is slightly greater than 90%. According to the current emission standards, it generally treats waste gas with a concentration of less than 800 mg/m³ and a temperature of less than 40°C.
 |
 |
 |
| Pillared activated carbon | Honeycomb activated carbon | Activated carbon fiber felt |
 |
 |
 |
| Granular Zeolite | Honeycomb zeolite | Zeolite wheel |
Desorption is the regeneration of the adsorbent, which refers to the process of separating the adsorbate from the adsorbent by means of high-temperature steam, hot gas purge, and pressure reduction.
2. Zeolite wheel adsorption principle
The zeolite adsorption wheel assembly (Cassette) is a central bearing and a supporting circular frame around the bearing that supports the rotor. The rotor is made of zeolite adsorption media and ceramic fiber. The wheel contains a seal for separating the treated exhaust gas and the clean gas released after treatment. The material is made of a soft material (usually silicon) that must be able to withstand the corrosiveness of VOCS and high operating temperatures. The seal separates the honeycomb zeolite adsorption wheel assembly into a basic adsorption zone (Adsorption zone) and a regeneration and desorption zone (Regeneration zone; desorption zone). However, in order to improve the adsorption treatment capacity of the wheel, it is common to add an isolation cooling zone (Cooling zone or Purge zone) to the first two zones. Usually, the adsorption zone is larger, while the desorption zone and cooling zone are two smaller treatment sides with equal areas. Sometimes it can be divided into more series zones for special needs, and the adsorption wheel is used with a set of electric drive equipment to rotate the wheel, so the wheel can have a variable speed during treatment and can control the ability to rotate 2 to 6 times per hour.
After the VOCs waste gas emitted by the factory enters the system, the first stage is to pass through a rotor composed of hydrophobic zeolite, and the VOCs pollutants are first adsorbed on the rotor; the second stage of the desorption process is to pass the waste gas (about 180 to 250°C) treated in the cooling zone that is preheated after heat exchange with the back-end incineration system into the rotor to desorb the organic matter at high temperature. At this time, the outflow pollutant concentration can be controlled to be about 5 to 20 times that of the inflow waste gas, and the desorbed organic matter can be incinerated at a temperature above 700°C in the third stage or condensed for recovery and reuse. This can reduce the size of the subsequent waste gas treatment unit, operating costs, and initial equipment costs.
The processing units of the zeolite wheel are as follows:
The body of the zeolite wheel is composed of some specific solid substrates coated with a layer of adsorbent powder. The substrate is made of ceramic, glass, or activated carbon fiber through sintering. Ceramic fiber is the most widely used because of its high temperature resistance, high thermal stability, washability, non-flammability, and acid and alkali resistance. The type of adsorbent varies depending on the gas composition to be treated. Generally, activated carbon, zeolite, etc., can be used. The thickness of the wheel is generally 25cm-45cm.
The matrix of the zeolite wheel is a ceramic fiber surface coated with a layer of adsorbent, generally activated carbon or hydrophobic zeolite, to form a honeycomb-shaped circular wheel, which is divided into two areas, namely the adsorption treatment area and the regeneration and desorption area. However, in order to improve the adsorption capacity of the wheel, sometimes a cooling area is designed between the two areas. Usually, the adsorption area is larger, and the desorption area and the cooling area are two smaller treatment areas of equal area.
Heat recovery equipment: After burning or oxidizing VOCs, the temperature of clean air is as high as 500-700℃. This part of the air is recovered through a heat exchanger to recover heat energy. At the same time, the clean air temperature is lowered and then directed to the desorption area of the rotor for desorption. If the temperature is too high, the rotor may burn. Therefore, the temperature entering the rotor should not be too high. Generally, two-stage heat recovery equipment is set up, and a blower is added to introduce fresh air and mix it with the burned air to control the desorption temperature within the range of 180-220℃. In order to treat VOC waste gas, in addition to the zeolite adsorption concentration rotor incineration system, a condenser is installed at the exhaust gas outlet to pre-divert and treat high-boiling-point VOCs (such as MEA, BDG, DMSO).
3. Principle of condensation recovery before and after activated carbon adsorption
The waste gas is collected by the collection system and enters the adsorption device for treatment.
During adsorption, the airflow enters the adsorption bed from the lower part of the bed, and the clean exhaust gas after adsorption is discharged through the exhaust pipe. After the adsorption reaches the set time, it switches to the desorption stage. During desorption, saturated steam enters the adsorption bed, and the solvent adsorbed in the bed leaves the adsorption bed together with the water vapor and enters the cooler.
The condensate is cooled to below 40°C, the non-condensable gas returns to the front of the fan for re-adsorption, and the solvent and condensed water enter the solvent storage tank for temporary storage.
According to the process requirements, the desorption time and intermittent time during automatic operation can be set through the touch screen, and the adsorption time is equal to the sum of the desorption time and the waiting time.
The equipment runs automatically without the need for personnel on duty. The electrical control system can be installed on-site or in the central control room. The maintenance workload is relatively small.
4. Introduction to the adsorption system
a. Exhaust gas pretreatment
According to the requirements of the design specifications, an emergency emission channel is designed and installed. The emission status is controlled by the production workshop to serve as a direct exhaust gas emission channel in case of an accident or equipment maintenance.
b Adsorption
The exhaust gas is sent into the activated carbon adsorber by the air intake fan. Under the action of the Van der Waals force, the organic solvent in the exhaust gas is captured and adsorbed by the micropores in the activated carbon. After the activated carbon is saturated with adsorption, it is regenerated. The exhaust gas is purified by the activated carbon adsorption and then discharged cleanly.
The adsorption tank specifications and adsorbent loading amount are designed according to the air volume to ensure a certain gas velocity and residence time, so that the adsorbent can effectively and fully absorb the organic solvent in the tail gas. The adsorption tank works alternately, and the working state of the adsorption tank is automatically switched by the PLC automatic control system to alternately perform the three processes of adsorption, desorption, cooling, and drying, and so on.
5. Process selection
The treatment process is selected after comprehensive analysis of the source, properties (composition, concentration, temperature, humidity), air volume, and other factors of the waste gas. Common treatment processes for treating large-volume, low-concentration organic waste gas are:
1) Zeolite adsorption, hot gas purge regeneration - catalytic combustion or high temperature incineration.
2) Activated carbon adsorption, water vapor or hot gas regeneration - condensation recovery.
3) Activated carbon adsorption, hot gas purge regeneration - catalytic combustion.
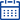
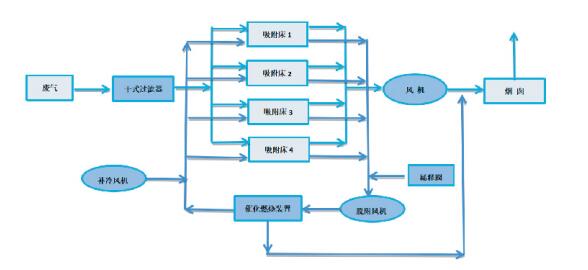 |
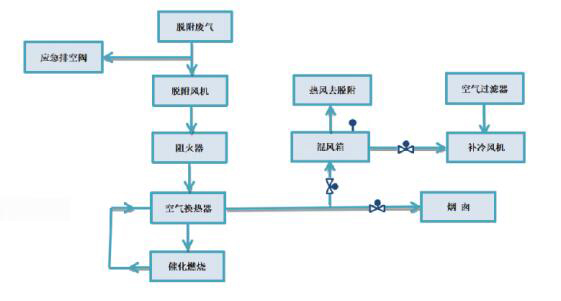 |
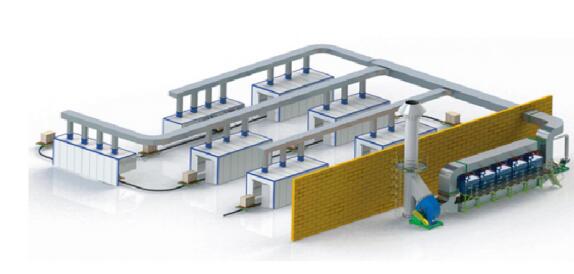 |
| Adsorption and desorption process flow chart | Desorption combustion process flow chart | Adsorption + catalytic combustion treatment equipment renderings |
Service unit customers
National Engineering Cases
Hangzhou Lvran Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd. is a comprehensive waste gas treatment system engineering service provider and equipment manufacturer, integrating R&D, technical services, design, production, engineering installation, and after-sales service.
We are China Catalytic combustion equipment Suppliers and Wholesale Catalytic combustion equipment Exporter, Company. The Group is a national high-tech enterprise, a Zhejiang Province science and technology enterprise, a regional R&D center, and an AAA-rated credit unit. It holds over 30 utility model patents, numerous invention patents, and software copyrights. The Group has long-standing technical R&D collaborations with domestic universities and institutions, including the "Environmental Innovation R&D Center" established with Anhui University of Science and Technology and the "Plasma Energy and Environmental New Technology R&D Center" jointly developed with Zhejiang Sci-Tech University. The Group has established its own R&D and production base for in-depth technical collaboration. The Group possesses core VOC gas treatment technology, holds a Level 2 general contracting qualification for municipal public works construction, a safety production license, a Class B special design qualification for environmental pollution control in Zhejiang Province, unclassified labor service qualifications, and specialized contracting for special projects. The Group is certified to ISO9001 for international quality, ISO14001 for environmental management, and ISO45001 for occupational health and safety.
 02 Feb,2026
02 Feb,2026
 22 Jan,2026
22 Jan,2026
 15 Jan,2026
15 Jan,2026
 08 Jan,2026
08 Jan,2026
 01 Jan,2026
01 Jan,2026