- 1 1. Introduction
- 2 2. Basic Concept of Filter Dust Collector
- 3 3. Working Principle of Filter Dust Collector
- 4 4. High-Efficiency Dust Removal Technology of Filter Dust Collector
- 5 5. Application in Workshop Air Purification
- 6 6. Dust Emission Standards and Compliance
- 7 7. Maintenance and Management of Filter Dust Collector
- 8 8. Future Development Trends
- 9 9. Conclusion
1. Introduction
In modern industrial production, dust has always been a significant challenge for both enterprises and environmental management. Whether in metal processing, woodworking, chemical production, or food processing, dust is constantly generated in the production environment. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of dust not only affects employees' health but also damages equipment operation and can even trigger safety incidents. Therefore, effectively controlling industrial dust has become an urgent task for enterprises.
In this context, the Filter dust collector serves as a mature and reliable industrial dust control device. It is widely applied across industries for dust management. It can efficiently capture fine dust in the air and ensure emissions meet environmental regulations, making it an essential core equipment for industrial dust control.
This article focuses on the Filter dust collector, covering its basic concept, working principle, high-efficiency dust removal technology, applications, and compliance with emission standards. Readers, including plant managers, environmental engineers, and industrial equipment technicians, can gain a comprehensive understanding and effectively implement Filter dust collector systems to optimize production environments and meet environmental goals.
2. Basic Concept of Filter Dust Collector
2.1 Definition of Filter Dust Collector
A Filter dust collector is an industrial dust removal device that separates dust particles from the air using filter media. Its core function is to capture dust on the surface of the filter and periodically remove or recover it, maintaining clean air.
Depending on the filtering method, Filter dust collector can be divided into various types:
- Baghouse filters
- Plate-and-frame filters
- Cartridge filters
Among them, baghouse filters are widely used in industrial dust control due to their large airflow capacity, adaptability to various dust types, and relatively low maintenance costs.
2.2 Difference from Other Dust Removal Devices
Compared to cyclone separators and electrostatic precipitators, Filter dust collector is more effective for fine dust removal. Cyclones rely mainly on centrifugal force to capture larger particles and are less effective for fine dust. Electrostatic precipitators, while capable of removing fine dust, have high complexity, high maintenance costs, and limitations regarding dust types. In contrast, Filter dust collector can handle both large and fine dust, making it ideal for high-concentration industrial environments.
2.3 Application Scope
Filter dust collector is widely used across industries:
- Metallurgy: High-temperature dust control in steel and aluminum plants
- Chemicals: Air purification in powder and granular chemical production
- Food processing: Dust control in flour, sugar, and grain production
- Woodworking: Dust collection in sawmills and furniture manufacturing
- Mining and building materials: Dust management in cement plants and stone processing
Regardless of dust type, Filter dust collector can be configured with different filter media and cleaning methods for efficient control.
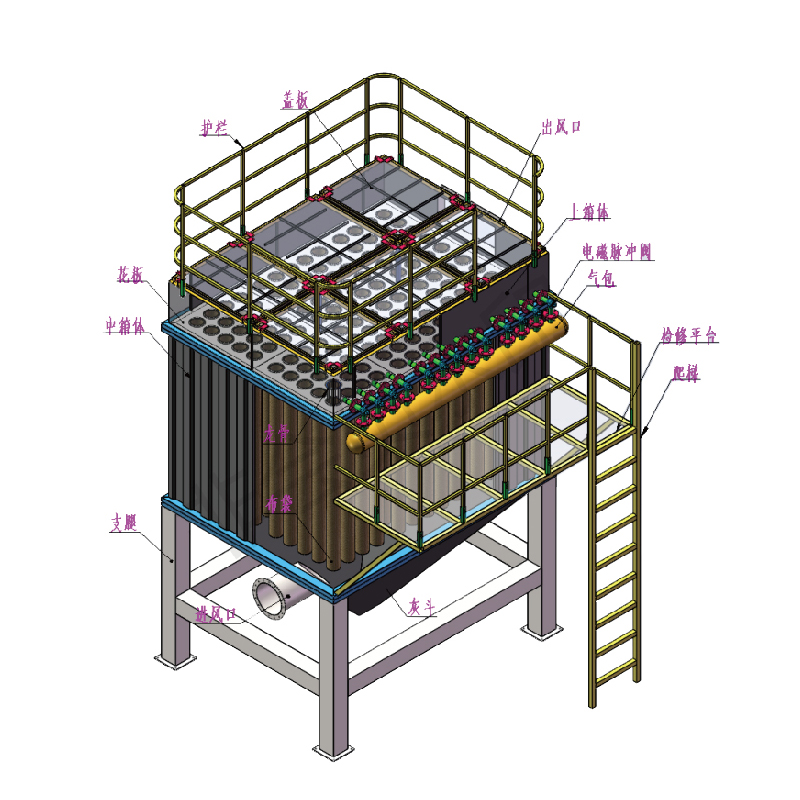
3. Working Principle of Filter Dust Collector
3.1 Baghouse Dust Collector Working Principle
Baghouse filters are the most commonly used type of Filter dust collector. Their working principle includes:
- Dust-laden air enters the collector: Dusty air generated from industrial processes is drawn into the collector through fans or natural airflow.
- Filtration through bags: Air passes through filter bags; dust particles are captured on the surface, while clean air passes through and exits.
- Dust accumulation and cleaning: Dust accumulates on the bag surface and needs regular cleaning into the hopper. Cleaning methods include reverse air, mechanical shaking, or pulse-jet cleaning.
- Clean air exhaust: Filtered air is extracted by fans and discharged into the environment or recirculated into the production area.
3.2 Factors Affecting Efficiency
Efficiency of a Filter dust collector depends on:
- Filter material: Fiber fineness, porosity, temperature, and corrosion resistance
- Air velocity and volume: Excessive speed can allow dust penetration; too low reduces efficiency
- Cleaning frequency: Untimely cleaning can cause blockage and reduce airflow
- Dust properties: Particle size, stickiness, and humidity influence filtration effectiveness
4. High-Efficiency Dust Removal Technology of Filter Dust Collector
4.1 High-Efficiency Filter Media
High-efficiency filter media are crucial for improving dust collection efficiency:
- Polyester felt: Suitable for general dust and high temperatures
- PTFE membrane filter bags: Ideal for fine or corrosive dust
- Glass fiber bags: High-temperature and mechanically strong, suitable for hot dust environments
4.2 Automatic Cleaning Systems
Modern Filter dust collector uses automatic cleaning systems such as pulse-jet cleaning, offering continuous bag cleaning, reduced wind resistance, improved efficiency, and lower labor costs.
4.3 Airflow and Pressure Control
Proper control of airflow and pressure ensures uniform dust deposition on bags, prevents local overload or penetration, and helps maintain stable operation over time.
5. Application in Workshop Air Purification
5.1 Industry Case Studies
- Woodworking: Captures wood dust in sawmills, improving worker comfort
- Flour processing: Recovers flour dust and reduces explosion risk
- Metal processing: Captures fine dust from welding and cutting, protecting equipment and safety
5.2 Air Purification Design Recommendations
Consider dust type, concentration, production layout, airflow requirements, and emission standards. Proper layout of Filter dust collector ensures efficient dust removal, energy savings, and reduced maintenance costs.
6. Dust Emission Standards and Compliance
6.1 Overview of Domestic and International Standards
- China: GB 16297-1996 and industry-specific standards, e.g., cement dust ≤30 mg/m³, steel dust ≤50 mg/m³
- Europe: Industrial Emissions Directive (IED 2010/75/EU), generally requiring ≤10–20 mg/m³
- USA: EPA NSPS standards specify limits for different industries and mandate high-efficiency dust control equipment
6.2 How Filter Dust Collector Achieves Compliance
- Optimized filter media: PTFE membrane or high-temperature glass fiber captures fine dust
- Precise airflow control: Ensures uniform dust deposition and prevents leakage
- Automatic cleaning: Pulse-jet cleaning maintains long-term efficiency
- Online monitoring: Real-time dust monitoring adjusts operations for continuous compliance
7. Maintenance and Management of Filter Dust Collector
7.1 Filter Bag and Media Maintenance
- Regular inspection: Replace damaged or aged bags
- Cleaning system maintenance: Ensure pulse-jet or mechanical cleaning functions properly
- Filter bag lifecycle management: Set replacement cycles based on dust type and working conditions
7.2 Fan and Duct Maintenance
- Duct anti-clogging: Inspect inlet/outlet to prevent airflow blockage
- Fan operation monitoring: Maintain stable airflow and pressure
7.3 Safety and Operational Guidelines
- Explosion prevention: Equip collectors with explosion-proof devices for flammable dust
- Personnel training: Ensure operators understand device principles, cleaning procedures, and safety
- Environmental management: Record dust emissions for regulatory compliance
8. Future Development Trends
8.1 Advanced Filter Media and Smart Materials
- Self-cleaning capabilities reduce manual maintenance
- Adaptation to high temperature and corrosive environments
- Nano-fiber materials for improved fine dust capture
8.2 Intelligent and Digital Management
- Remote monitoring of airflow, pressure, and emission levels
- Automatic cleaning adjustment based on dust concentration
- Predictive maintenance to reduce downtime
8.3 Energy and Environmental Optimization
- Low-pressure-loss design to reduce fan energy consumption
- Dust recovery systems for resource recycling
- Compliance with stricter emission standards
8.4 Enhanced Multi-Industry Adaptability
- Suitability for high-temperature, high-humidity, and corrosive environments
- Capturing ultrafine dust in electronics and pharmaceutical industries
- High airflow capacity for large-scale industrial production
9. Conclusion
Filter dust collector is indispensable in modern industrial dust control. Through the detailed analysis of its concept, working principle, high-efficiency technology, workshop applications, emission standards, and maintenance, it demonstrates how enterprises can achieve:
- Efficient dust capture: Using suitable filter media and cleaning methods for fine dust control
- Workshop air purification: Improving working environment and employee health
- Emission compliance: Maintaining standards with proper design and operational control
- Long-term energy efficiency and reliability: Intelligent management and energy-saving design reduce operational costs
- Future development potential: Advanced media, smart control, and environmental technology enhance industrial dust control capabilities
Enterprises should combine Filter dust collector selection and application with their production processes, dust characteristics, and environmental requirements to create a scientifically designed dust control plan, fully realizing safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly production.





 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体








